According to the University of California, San Diego, the average American consumes about 34 gigabytes of data and information every day. And here's what you can do with that much data:
- Stream every episode of Stranger Things (25 episodes, ~1GB each)
- Play over 15,000 hours of Fortnite (500 hrs/GB)
- Scroll for 94 hours on TikTok (2.7 hrs/GB)
That's as much information as a highly educated person would have processed in their entire lifetime 500 years ago.
Considering this statistic is from many years ago, it's concerning to think about how much information we consume today.
The history of news - Everything you didn’t know
If you're a data enthusiast, you might think, "Who cares? I enjoy getting the equivalent of 16 movies pumped into my brain daily, like a never-ending buffet."
Well, maybe you should care. Information overload is real, and consuming too much info can be harmful. Studies have found several effects of information overload, including:
- Difficulty focusing
- Lower productivity
- Increased stress
- Forgetfulness
- Poor decision-making
- Easy spread of misinformation
- Harder to trust sources
These factors make it difficult to determine if information is true, and your credibility depends on using accurate info. If you use info that others know is wrong, you'll be less trustworthy, making it tough for others to believe you later.
If you want to avoid losing credibility and don't want to share inaccurate information - whether with friends or at work - you need to learn how to conduct online research and go beyond just Google search results.
The most common oversights of online research
Conducting online research can be both exciting and overwhelming and it largely depends on how you approach it, how you organize the information you find, and whether it's easily accessible to you.
To get the most out of your online research, we've highlighted the key mistakes you should avoid:
➡️ Ignoring publication dates
➡️ Overlooking biases
➡️ Relying solely on abstracts or summaries
➡️ Not verifying facts
➡️ Misinterpreting data
➡️ Failing to use advanced search techniques
➡️ Neglecting primary sources
➡️ Not keeping track of sources
➡️Overlooking context
Not evaluating sources for credibility
Not evaluating sources for credibility means not checking if the information you're using comes from a trustworthy and reliable source.
If you want to improve your knowledge or, even better, share and use the information you've found, you need to be sure it's accurate. It's important to check who created the content, their expertise, and if the information is backed by evidence.
If the source is biased, outdated, or not reliable, the information might not be correct or trustworthy.
Always choose well-known, trusted sources like peer-reviewed journals, reputable news outlets, and official organization websites to make sure you're getting reliable information. Blogs, forums, and social media posts, on the other hand, may contain biased or unverified information.
Ignoring publication dates
Ignoring publication dates in research means not paying attention to when the information was published.
This can be a problem because some information, especially in fields like technology or medicine, can quickly become outdated. What was true a few years ago might no longer be accurate today.
Always check the publication date to ensure the information you're using is still relevant and up-to-date for your research.
Overlooking biases
Overlooking biases is when you don't consider how the author's personal opinions, beliefs, or perspectives might influence the information they present.
Everyone has some level of bias, whether intentional or not, and it can affect how facts are interpreted or shared. When doing research, it's important to be aware of any potential biases in your sources and try to balance them by consulting a variety of viewpoints.
Relying solely on abstracts or summaries
Abstracts and summaries can be useful, but they often miss key details. Whenever you can, make sure to read the full text to get the complete picture and fully understand the context and findings.
It's always better to go beyond the summary to get the most accurate and complete view.
Not verifying facts
Failing to verify facts happens when you don't double-check the information you come across.
It's important to cross-check facts and statistics with multiple trusted sources to ensure they're accurate. If one website makes a claim, look for other reputable sites that support the same information.

Misinterpreting data
Misinterpreting data is common, especially if you're not familiar with the methods used to collect and analyze it. Make sure to pay attention to how the data was gathered and examined.
If you're unsure, it's a good idea to consult experts to help you understand it better.
Failing to use advanced search techniques
Using advanced search techniques in your research can make a big difference in finding the right information for your assignment.
Here’s how:
- Finding what you need: Search techniques like using "AND" or "OR" and putting phrases in quotation marks help the search engine know exactly what you're looking for. This way, you get more accurate results that are directly related to your assignment.
- Cutting out the irrelevant stuff: The internet is full of information that may not be useful for your work. By using filters and limiters, you can narrow down your search to things like recent articles, scholarly sources, or specific topics. This helps you focus on what's important.
- Saving time: Instead of wasting hours scrolling through irrelevant pages, search techniques help you find useful info faster. You can quickly find reliable sources and spend more time working on your assignment.
- Getting the best results: By using the right keywords, trying out synonyms, and experimenting with different search strategies, you can find a wide range of helpful information. This helps you understand your topic better and create a stronger assignment.
Neglecting primary sources
Primary research is a type of research where you collect data yourself, instead of relying on existing information. You gather first-hand details that help with decision-making or guide the next steps in your research.
Whenever you can, go straight to the original sources, like research papers, official documents, or firsthand accounts. Secondary sources might misinterpret or oversimplify the original information.
Not keeping track of sources
If you want to keep track of your sources, you need to find a way to systematically collect, organize, and use content from different places like websites, PDFs, and social media.
Keeping track of your sources is important for a few key reasons:
- Efficiency: When your resources are organized, you save time and can quickly find what you need.
- Collaboration: Good resource management makes it easier for teams to work together since everyone can easily access and share information.
- Decision-making: Having well-organized resources means you can make informed choices based on accurate and readily available data.
- Productivity: Streamlined workflows help you and your team focus on what matters, reducing the time wasted searching for info.
- Knowledge retention: Managing your resources well ensures that knowledge is preserved and easy to find later, helping everyone learn and grow over time.
Without proper tracking, it becomes difficult to verify facts and find the sources again when you need them.

Overlooking context
Without understanding the context, it’s easy to misinterpret the data or draw wrong conclusions.
You need to think about how the data was collected, the conditions it was gathered under, and the purpose behind it. If you don’t, the data might not be reliable and could affect your future analysis.
Actionable steps for deeper insights
To get deeper insights and ensure the information you find is reliable, it's helpful to use techniques like the 5Ws, SMART Check, and the CRAAP Test. These methods are great for digging deeper and checking the quality of the data.
5Ws
Asking these five questions helps evaluate the credibility and reliability of a source, as they cover the most important factors:
- Who is the author? (Authority)
- What is the purpose of the content? (Accuracy)
- Where is the content from? (Publisher)
- Why does the source exist? (Purpose and objectivity)
- How does this source compare to others? (Determining what’s what)
SMART check
This method helps evaluate newspaper sources and involves asking important questions about the source:
- Source: Who or what is the source?
- Motive: Why do they say what they do?
- Authority: Who wrote the story?
- Review: Is there anything that seems potentially untrue?
- Two-source test: How does it compare to another source?
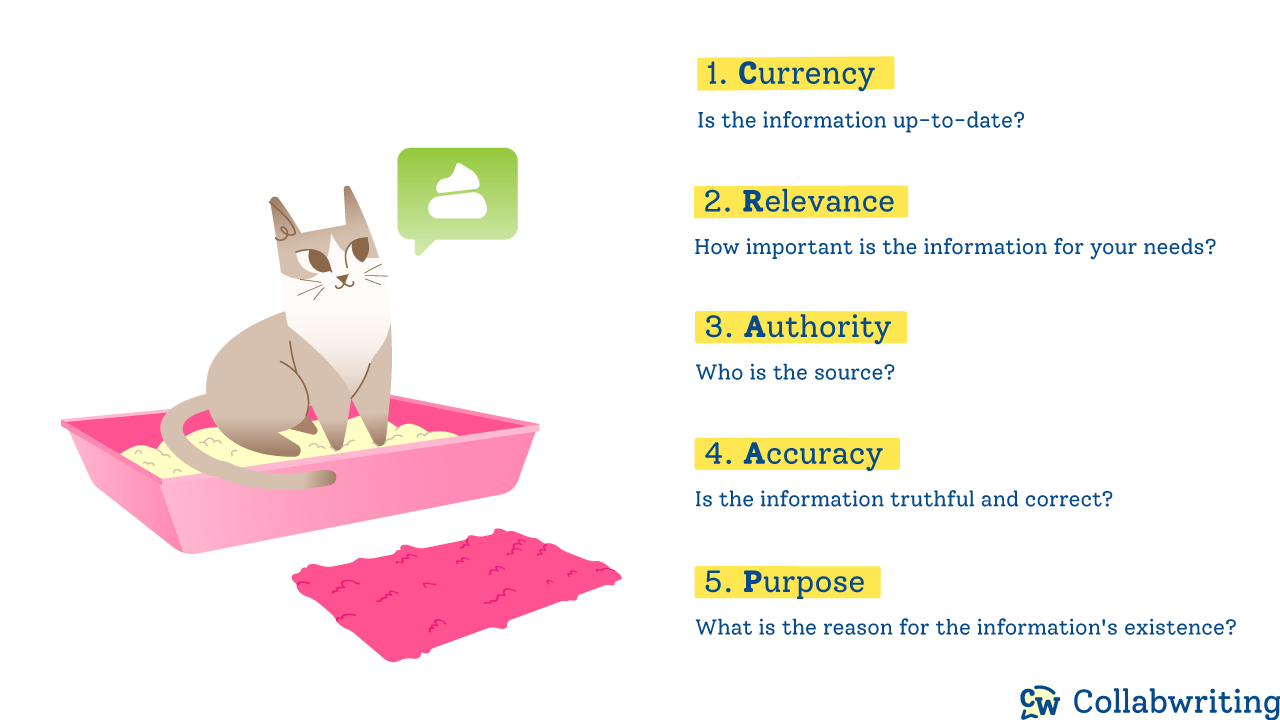
CRAAP test
This method provides a set of guidelines to help you evaluate the credibility of a source:
- Currency: Is the information up-to-date?
- Relevance: How important is the information for your needs?
- Authority: Who is the source?
- Accuracy: Is the information truthful and correct?
- Purpose: What is the reason for the information's existence?
Closing thoughts
Ethical research practices are essential for building credibility and trust in the information we both consume and share.
Research is rarely quick or easy; it requires thoughtful planning, careful attention, and a clear sense of purpose. By approaching research with intention, clarity, and a strong commitment to ethical standards, we can produce work that stands up to scrutiny and serves others.

Collabwriting - Shareable Notes on Web Pages and PDFs
Create shareable notes and highlights on any web page, PDF, YouTube, or Kindle - Organize and collaborate on your research or create a knowledge base.
FAQ
Why is evaluating the credibility of sources important in online research?
Evaluating sources helps ensure the information you're using is accurate and trustworthy. If you rely on unreliable sources, your own credibility could be hurt.
How can I tell if the information I find is up-to-date?
Check the publication date! Some information, especially in fields like tech or medicine, can become outdated quickly. Always make sure the source you're using is recent enough to be relevant to your research.
What is the best way to avoid biases in my research?
Everyone has their own perspective, but looking at multiple viewpoints can help you get a more balanced, accurate understanding of the topic.
Why should I go beyond abstracts or summaries in my research?
Abstracts and summaries can leave out important details. To fully understand the topic, it's best to read the entire source so you don’t miss key information that could change your conclusions.






![The Best Tool for Collaborative Research in Content Marketing Teams [2026]](/content/images/2025/12/image--5-.png)
![5 Tools Marketers Use to Organize Research - Compared [2026]](/content/images/2025/11/cover-4-1.png)

![Build Credibility in Research: Smart Way to Verify Information and Track Sources Easily [2025]](/content/images/2025/10/covers-for-blog--7--1.png)
![How Marketers Can Turn LinkedIn Content into Collaborative Research [2025]](/content/images/2025/10/covers-for-blog--8-.png)
![Best Readwise Alternative for Personal & Team Research [2026]](/content/images/2025/09/Frame-814--3-.png)