Do you ever feel like there’s important information within your team or organization that you should know, but it keeps slipping through your fingers?
Research shows that employees spend hours searching for information they need.
That’s why all teams - big or small - must find an effective way to keep important information within the organization so it’s always accessible. This doesn’t just help current employees but also benefits new ones as they join.
What’s organizational knowledge?
Organizational knowledge represents all the information, skills, and experience everyone in a company has. It includes:
- Tacit knowledge: Personal knowledge that’s a bit hard to express, like individual experiences, insights, and skills.
- Implicit knowledge: This is knowledge that everyone in the organization understands and uses such as best practices or unwritten rules, but it’s not formally written down.
- Explicit knowledge: Things that are written down and easy to share - manuals, databases, procedures, and policies.
- Declarative knowledge: Factual knowledge - information about theories, concepts, or facts on a specific subject.
- Procedural knowledge: Knowledge about processes and how to carry out tasks step-by-step.
- Individual knowledge: Knowledge each person has based on their own experiences and skills.
- Collective knowledge: This is knowledge that comes from working together as a team, sharing experiences, and collaborating with others.
Managing organizational knowledge means ensuring the information is captured, shared, and used effectively. This helps the company make better decisions and work more efficiently.
4 key elements of organizational knowledge
Organizational knowledge is what helps a business grow and stay competitive. It consists of skills, experiences, data, and intellectual property. When used well, these elements improve decision-making and support long-term success.
- Skills: Employees' specific abilities that help them do their jobs well. These include both technical skills and soft skills like communication and teamwork.
- Experiences: Practical knowledge gained from everyday work that aids in decision-making and process improvement. This often provides insights that formal training doesn’t cover.
- Data: This includes all the quantitative and qualitative information that organizations collect and analyze to make informed, data-driven decisions.
- Intellectual property: Patents, trademarks, copyrights, and confidential processes that give the organization a competitive edge. Managing intellectual property is essential for staying competitive and complying with regulations.
Organizational knowledge management
Organizational knowledge management is the process of finding, documenting, storing, and using knowledge to improve business performance.
Here’s what it usually involves:
- Highlighting knowledge: Identifying where knowledge exist, whether it's with individuals, within teams, or embedded in processes.
- Capturing knowledge: Documenting important and accurate information to share with others.
- Storage and organization: Using systems such as databases or platforms like Collabwriting to make information easy to access, retrieve, and keep secure.
- Applying knowledge: Turning data and information into actionable insights that are easy for everyone to understand and use.
9 key steps to effectively manage organizational knowledge
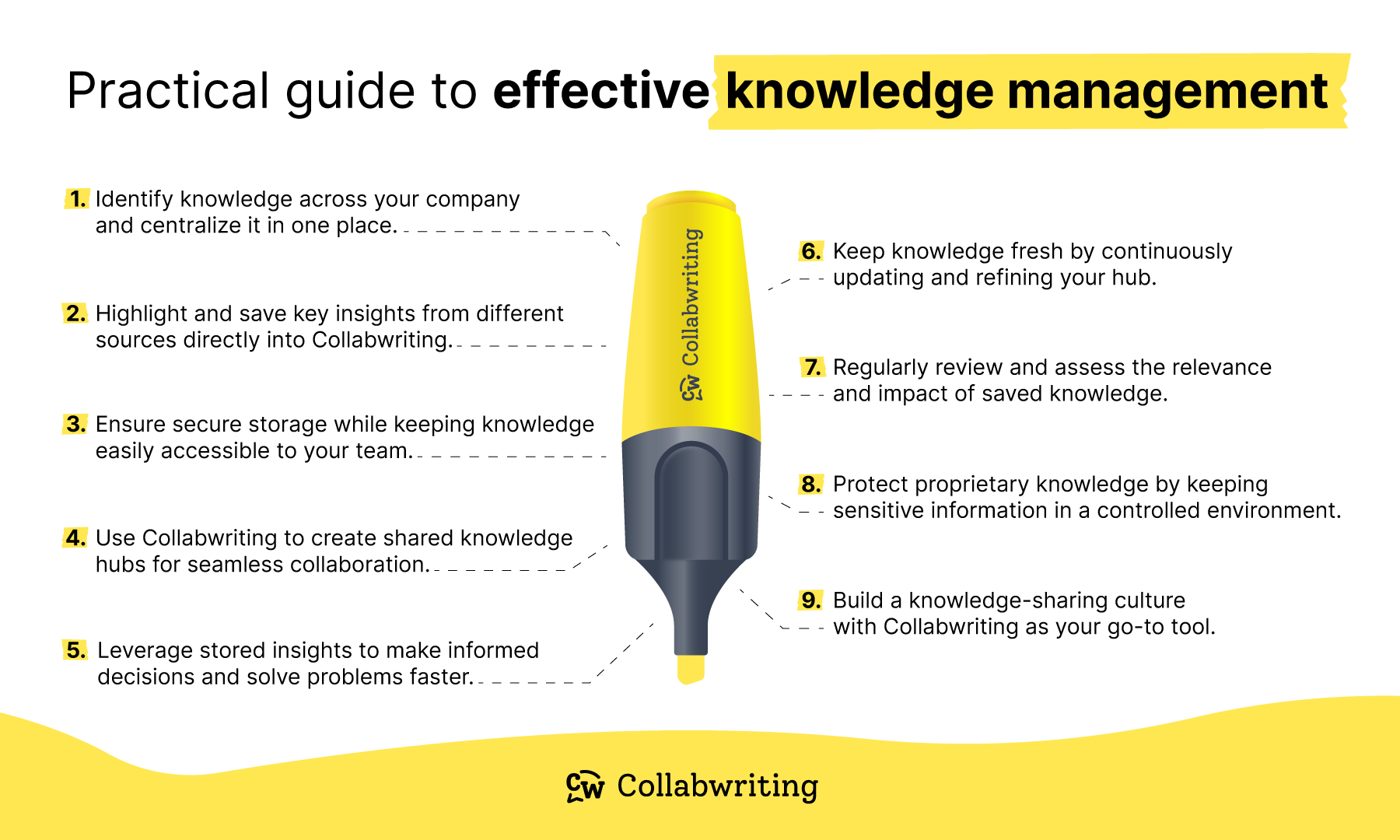
Step 1: Map out the current knowledge within your company
Identify the most valuable knowledge and where it’s stored - whether with individuals, teams, or systems. Use tools like a skills matrix or knowledge audit to map knowledge and spot gaps.
Knowledge mapping (like flowcharts) can help organize and make knowledge more accessible, while a skills matrix shows individual expertise.
Involve employees in this process to promote knowledge sharing, avoid silos, and tap into expert insights to help everyone grow.
Tip: You can kick off this process by holding meetings with employees to gather information about job-related knowledge and then follow up on other identified knowledge areas.
Step 2: Collect and organize key knowledge points
Once you’ve identified and mapped out existing knowledge, document it in a clear and accessible way. For example, if you document a project guideline, make sure it covers common questions and is stored on a platform everyone can access.
Unstructured knowledge, such as meeting notes, emails, or team chat messages, is also valuable. Agree on the best way to organize and store this information, and continue managing it effectively.
Tip: Marketers can make it easier by setting up simple guidelines for capturing and organizing knowledge, so everyone stays on the same page.
Step 3: Keep knowledge secure while ensuring easy access for authorized users
Organizational knowledge needs secure storage that’s easy for authorized users to access.
Using tools like knowledge bases, cloud storage, or platforms like Collabwriting can make this easier. The key is to organize the knowledge simply and intuitively for everyone who needs it.
Tip: Help the team choose the right platform, show everyone how to use it, and remind them to keep all information confidential.
Step 4: Choose tools that support sharing knowledge
Sharing knowledge helps everyone learn from each other’s experiences.
Choose a tool that supports knowledge sharing easily. No one likes tools that aren’t intuitive, so make sure the choice is a good one.
Tip: Using Collabwriting, create a weekly learning topic where all team members can add useful information. This way, everyone can share insights, resources, and ideas in one place, making it easy for the whole team to learn and grow together.
Step 5: Draw on knowledge to make decisions and find solutions
Integrate knowledge into decision-making across the organization. One great way to do this is by using data analytics tools or knowledge databases whenever important decisions are being made.
Tip: Encourage better decision-making by helping employees and leaders understand how to find and use relevant knowledge quickly. For example, guide them on using internal resources to solve problems.
Step 6: Keep knowledge up-to-date
Set up a process to regularly review stored knowledge. Removing outdated information can help prevent 'information overload' and keep your team focused on what matters.
Tip: Create a plan for regular check-ups on knowledge resources to keep everything current. Also, teach employees how to filter out outdated info and keep what’s most important, especially when big updates happen.
Step 7: Evaluate the relevance of knowledge
Regularly check the quality and relevance of your organization’s knowledge to see how it’s helping individuals, teams, and the business as a whole.
Relevant knowledge supports better decision-making, while irrelevant info just makes things harder to find.
Tip: Hold regular check-ins, like team meetings or one-on-one conversations, to ask how employees are using the knowledge and if it’s helpful. This will help you identify areas for improvement or changes that may be needed.
Step 8: Secure sensitive knowledge
Work with your IT team to implement security measures that protect sensitive information. Ensure employees only have access to what they need for their role.
Tip: Want to share your work with others? Collabwriting makes it easy! You can control who can view and edit your content, so you're always in charge.
Step 9: Foster a knowledge-sharing culture
Promote open communication and recognize employees who share knowledge. This helps build trust between everyone in the organization.
Tip: Set up programs or activities that show how valuable knowledge sharing is. You could also offer workshops or team exercises to get everyone involved in sharing what they know.
The benefits of organizational knowledge management
When organizations effectively manage and share knowledge, they can unlock the full potential of their teams and processes. Here are some key benefits:
➡️ Improved agility: Quickly adapt to changes and seize new opportunities.
➡️ Better decision-making: Access accurate information to make fast, well-informed decisions.
➡️ Faster problem-solving: Use existing knowledge to solve issues quickly.
➡️ More innovation: Encourage creativity and share new ideas.
➡️ Employee growth: Provide resources for continuous learning and development.
➡️ Access to expertise: Make specialist knowledge available to everyone.
➡️ Better communication: Enhance clear and effective communication across teams.
➡️ Improved processes: Streamline operations and boost efficiency.
What to do next?
The first step is to pick the right tool that fits your team’s needs. Once you have the tool, make sure everyone understands how important it is to use technology for managing knowledge.
Collabwriting is a great option because it's easy to use. It works well for many industries like marketing, legal, consulting, and R&D.
However, it's always a good idea to try it out and see if it works for you and your team.

Collabwriting - Shareable Notes on Web Pages and PDFs
Collabwriting allows you to gather all your online sources in one place. Just highlight, save, and collaborate with anyone on any content you find online.
FAQ
Why is organizational knowledge management important?
Organizational knowledge management is essential for getting the most out of your team's collective intelligence. It helps everyone make better decisions, work more efficiently, and come up with innovative ideas.
What is organizational knowledge?
Organizational knowledge encompasses all the information, skills, and experience within a company. It includes: tacit, implicit, explicit, declarative, procedural, individual, and collective knowledge.
What are the key elements of organizational knowledge?
The key elements of organizational knowledge are: skills, experiences, data and intellectual property.
How can we effectively manage organizational knowledge?
Effective knowledge management involves:
- Highlighting knowledge: Identifying where knowledge exists within individuals, teams, or processes.
- Capturing knowledge: Documenting important information accurately.
- Storage and organization: Using systems like databases or platforms (e.g., Collabwriting) for easy access and security.
- Applying knowledge: Converting data into actionable insights.
How does Collabwriting help with knowledge management?
Collabwriting allows teams to gather, save, and collaborate on online content in one place. It’s easy to use and effective for many industries, supporting seamless knowledge management and collaboration.




![The Best Tool for Collaborative Research in Content Marketing Teams [2026]](/content/images/2025/12/image--5-.png)
![5 Tools Marketers Use to Organize Research - Compared [2026]](/content/images/2025/11/cover-4-1.png)

![Build Credibility in Research: Smart Way to Verify Information and Track Sources Easily [2025]](/content/images/2025/10/covers-for-blog--7--1.png)
![How Marketers Can Turn LinkedIn Content into Collaborative Research [2025]](/content/images/2025/10/covers-for-blog--8-.png)
![Best Readwise Alternative for Personal & Team Research [2026]](/content/images/2025/09/Frame-814--3-.png)